
Controlling Pathogenic Bacteria in Shrimp with Probiotics
| Wed, 08 Sep 2021 - 10:01
This article, adapted and abstracted from the Restrepo et al. 2021 study, characterizes the microbial community of shrimps treated with the probiotic Vibrio diabolicus ILI after challenge testing with pathogens hepatopancreatic necrosis (AHPND).
One of the pathogens causing significant economic losses to shrimp farming is acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND). The causative agent of this disease is Vibrio bacteria containing the plasmid pV-AHPND. AHPND causes severe damage to hepatopancreas cells, resulting in mass death of shrimp.
The severity of AHPND and the limitation of antibiotics forced researchers to develop alternatives, such as the application of probiotics. To evaluate the potential of using probiotics to limit the harmful effects of bacteria causing hepatopancreatic necrosis disease, Restrepo et al in 2021 evaluated the effects of ILI strain ( Vibrio diabolicus) and evaluated their impact on shrimp after challenge with pathogenic bacteria V. parahaemolyticus .
Read more: Methods of Controlling Vibrio in Shrimp Ponds
Effects of Probiotics in Aquaculture
Probiotics are microorganisms that confer a beneficial effect on their host, by preventing the colonization of pathogenic bacteria through an antagonistic action or stimulation of the host's immune system. The use of probiotics is a promising alternative to antibiotics and a way to treat and prevent disease in farmed shrimp.
The choice of probiotics can be controversial in some cases, especially in aquaculture where several genera of bacteria used as probiotics are closely related phylogenetically. (a group of organisms with a common ancestor) with pathogenic bacteria. For example, in shrimp hatcheries in Ecuador, beneficial strains of Vibrio alginolyticus and AHPND- causing strains of Vibrio parahaemolyticus belong to the same phylogenetic clade.
In particular, a strain formerly known as V. alginolyticus ILI strain (which in this study classified them as Vibrio diabolicus ) was isolated from healthy shrimp larvae and proved to be an effective probiotic.
The Restrepo et al. 2021 study used the probiotic strain ILI ( Vibrio diabolicus ) which is known to be a probiotic. This strain was initially isolated from the water of a healthy shrimp hatchery.
Read more: Research Backs Value of Probiotics in Shrimp Ponds
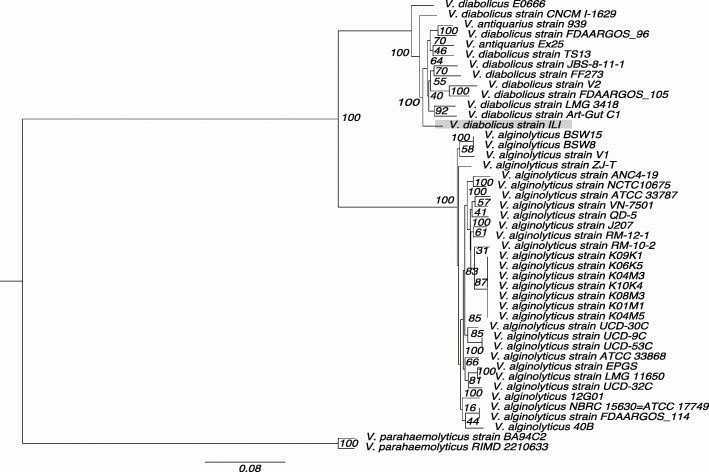

Subspecies Vibrio diabolicus ILI. The plant includes 10 strains of Vibrio diabolicus, 20 strains of Vibrio alginolyticus, 2 strains of Vibrio antiquarius, and 2 strains of Vibrio parahaemolyticus as outgroups.
Using Probiotic Strain ILI ( Vibrio diabolicus ) in Shrimp Culture
After feeding white shrimp with a probiotic supplement ( Vibrio diabolicus ILI), the survival rate of shrimp challenged with V. parahaemolyticus BA94C2 strain and changes in the structure of the microbial community on the stomach shrimp and hepatopancreas were also evaluated.
Immune-related organs - blood cells, hepatopancreas and gills - are important in the response to AHPND. And colonization of the stomach is the first step in the process of infection with the Vibiro bacteria that cause AHPND.
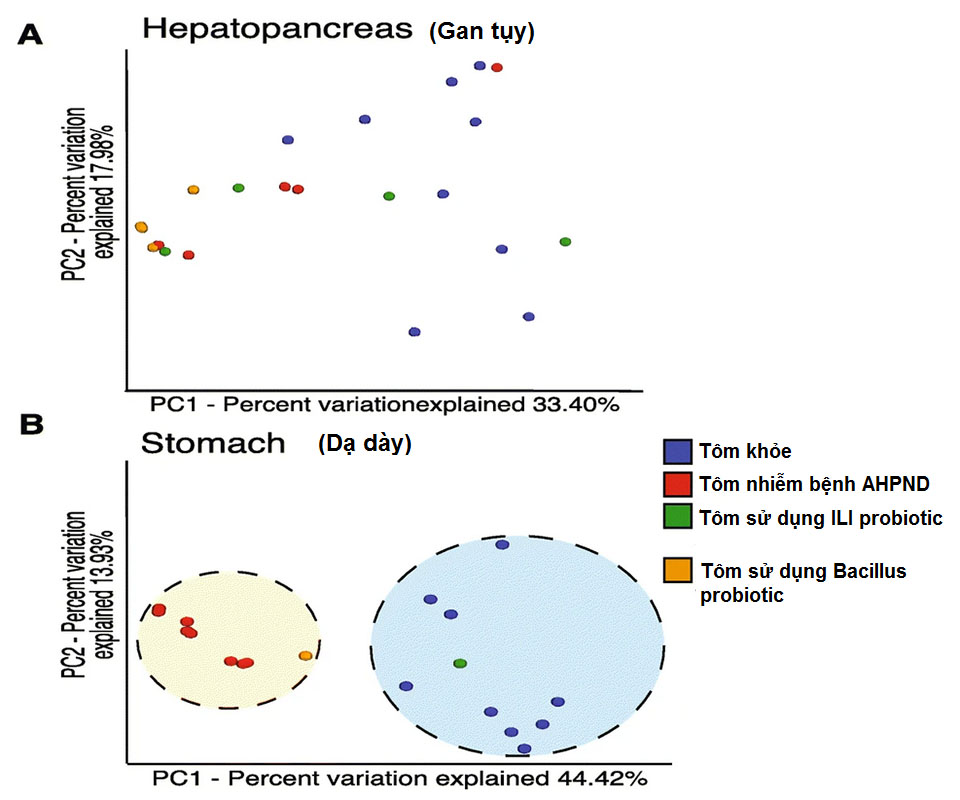
Diversity analysis of microbiota from hepatopancreas and stomach samples.
A) Principal component analysis showed no clear clustering between the 4 different experimental methods for hepatopancreatic samples.
B) The PCoA plot shows a clear clustering of the gut microbiota of infected shrimp compared with healthy shrimp. When using ILI probiotics, the shrimp microbiota was similar to that of healthy shrimp.
Read more: Using Bacillus to Inhibit Pathogenic Vibrio Harveyi Bacteria in Farmed Shrimp
The use of probiotics in aquaculture is a practical alternative to promote animal health and prevent disease. Research shows that the use of microbial probiotics such as ILI can modulate the host microbiota and may contribute as a promoter to some potentially probiotic species by inhibiting colonization that colonize the gastrointestinal tract of pathogens. The microbiome alteration induced by a successful probiotic can control pathogenic populations in the shrimp gastrointestinal tract and stimulate survival in aquaculture.
Strain V. diabolicus ILI is a bacterial strain isolated from shrimp larval culture that has shown antibacterial activity against many pathogenic strains of other Vibrio species . This study shows that ILI supplementation to vannamei helps maintain a healthy microbial community in the gastrointestinal tract of shrimp after being challenged with AHPND pathogenic bacteria.
This finding suggests that strain ILI can be used as a probiotic to reduce the population of AHPND bacteria causing hepatopancreatic necrosis disease in shrimp, increasing survival and resistance to this important pathogen in shrimp. shrimp farming, without the risk of becoming pathogenic.
Source: tepbac.com






















